Sweat happens—it’s a natural part of life. But when it comes to staying fresh, the terms "antiperspirant" and "deodorant" are often used interchangeably, creating confusion and frustration when these underarm products don’t deliver the expected results. Are you looking to tackle sweat stains, control body odor, or both? Understanding the difference between these products and how they address sweat production and odor can help you choose the better option for your needs.
So, let’s clear the air on sweat control and odor protection, so you can approach your hygiene routine with confidence.
The Problem: Sweat and Smell
Sweating is essential for regulating body temperature, but not all sweat is the same.
What Causes Sweat?
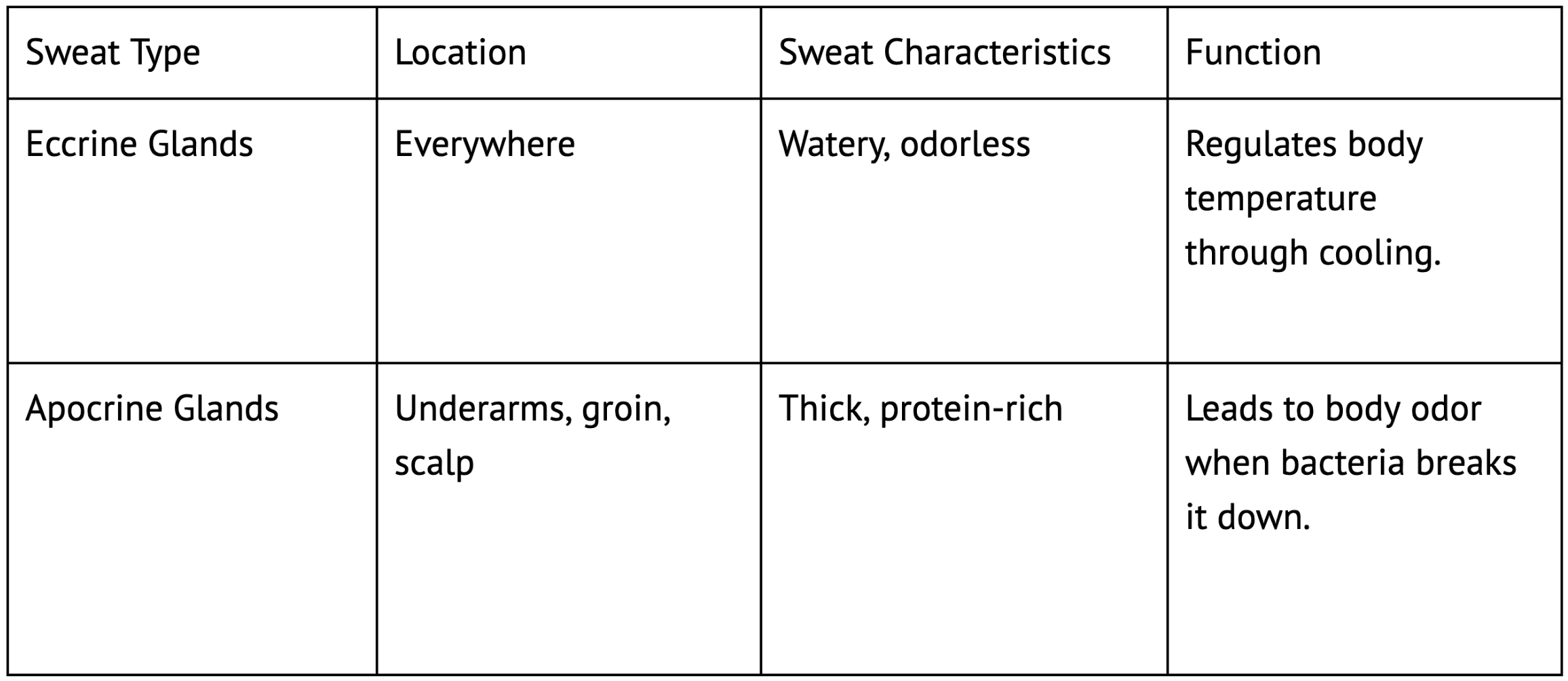
Sweat comes from two main types of sweat glands in your skin:
Eccrine Glands: These are found all over the body and release watery, odorless sweat. They play a key role in cooling the body during perspiration from exercise, heat, or stress.
Apocrine Glands: Concentrated in the armpits, groin, and scalp, these glands produce thicker, protein-rich sweat. While this sweat is initially odorless, it becomes the culprit behind underarm odor when broken down by bacteria on the skin.
Sweat vs Odor: What’s the Key Difference?
The moisture from eccrine sweat glands isn’t the source of odor, it’s actually the breakdown of apocrine sweat by bacteria that creates sweat odor.
Antiperspirants: Solving Sweat
How Do Antiperspirants Help?
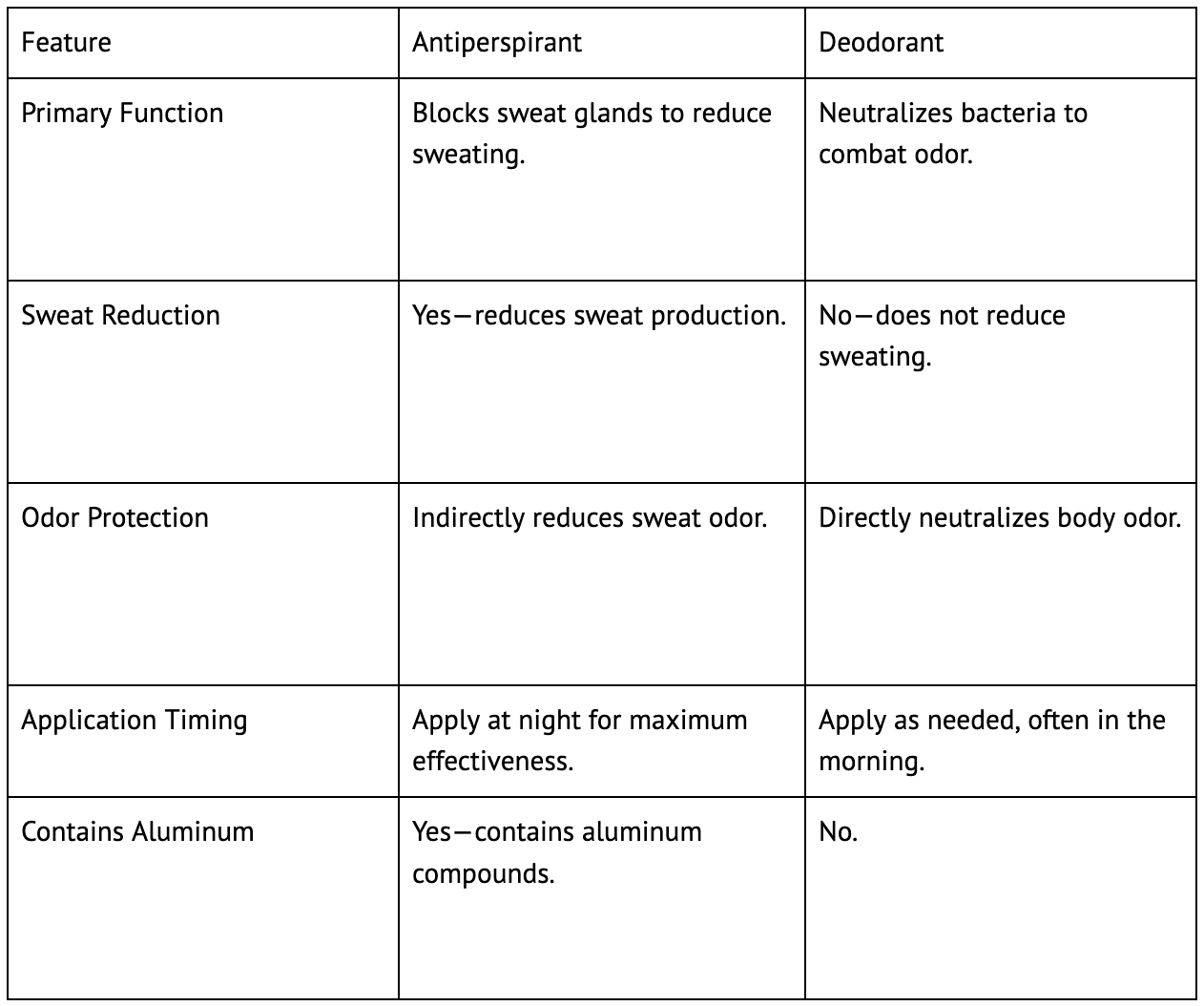
Antiperspirants are designed to reduce sweat production by temporarily blocking sweat ducts, using active ingredients like aluminum salts (e.g., aluminum chloride or aluminum chlorohydrate) that form a gel-like plug in the sweat pores, reducing the amount of sweat released onto the skin. This process is highly effective in controlling excessive sweating, keeping the skin dry, and preventing sweat stains.
When Should You Use Antiperspirants?
Antiperspirants are ideal for situations where sweat control is a priority:
Hot weather or high humidity, when sweat protection is essential.
Stressful events like job interviews or public speaking.
Managing conditions like hyperhidrosis, where sweating occurs excessively.
Myths About Antiperspirants
Myth: "Antiperspirants cause breast cancer."
Reality: Numerous studies, including those by the American Cancer Society, show no proven link between antiperspirants containing aluminum compounds and breast cancer.
Myth: "Antiperspirants trap toxins in your body."
Reality: Sweat isn’t responsible for detoxifying your body—that’s your liver and kidneys’ job. Perspiration primarily cools the body.
Tips for Using Antiperspirants Effectively
Apply at Night: Antiperspirants work best when applied to clean, dry skin before bed, as this allows the aluminum salts to form plugs overnight.
Avoid Irritated Skin: Applying antiperspirants to freshly shaved or waxed underarms can cause skin irritation, so you'll want to wait a few hours before application.
Layer Lightly: A thin layer is enough for effective sweat reduction without residue.
Reapply Strategically: For particularly sweaty days, you can reapply antiperspirant as needed.
Deodorants: Fighting Odor
How Do Deodorants Help?
Deodorants don’t affect sweat production, rather they’re all about odor control. They do this in two ways: 1) by targeting bacteria on the skin, some deodorants neutralize the breakdown of sweat that leads to body odor and 2) by including fragrance to keep you smelling fresh throughout the day.
Unlike antiperspirants, however, deodorants are not designed to block sweat glands, so they won’t reduce moisture levels.
When Should You Use Deodorants?
Deodorants are perfect for managing odor protection without reducing sweat and work best in the following scenarios:
Normal or mild sweating: When your goal is to smell fresh rather than stay dry.
Daily use: Ideal for everyday activities like office work, low-intensity exercise, or casual outings.
Sensitive skin: Many natural deodorants are free of harsh chemicals, making them suitable for sensitive underarms.
Types of Deodorants
There’s a wide variety of deodorants to choose from:
Traditional Deodorants: These include synthetic antibacterial agents and long-lasting fragrance.
Natural Deodorants: These use ingredients like baking soda, cornstarch, or essential oils and are free of aluminum salts.
Tips for Using Deodorants Effectively
Choose the Right Formula: If you have sensitive or irritated skin, opt for hypoallergenic or natural deodorants.
Combine with Antiperspirants: Layering deodorant over antiperspirant offers dual benefits for dryness and freshness.
Reapply as Needed: Deodorants may need to be reapplied after heavy physical activity or during warm weather.
Apply to Dry Skin: For maximum effectiveness, make sure your underarms are completely dry before applying deodorant.
Antiperspirants vs. Deodorants: The Key Differences
Understanding the key difference between antiperspirants and deodorants is crucial for choosing the right product.
Prescription Treatments for Excessive Sweating
For some individuals, over-the-counter, or OTC, antiperspirants and deodorants may not provide enough relief from excessive sweating, also known as hyperhidrosis. If sweat continues to disrupt daily life, despite your best efforts, it may be time to explore prescription treatments.
Prescription Antiperspirants
Stronger than their OTC counterparts, prescription antiperspirants often contain higher concentrations of aluminum chloride or aluminum chlorohydrate, which work by deeply penetrating the sweat ducts to block sweat production effectively. These antiperspirants are typically applied at night, allowing them to work while sweat glands are less active.
Oral Medications
For more generalized sweating, or cases that affect multiple areas of the body, doctors may prescribe oral medications. These medications, such as anticholinergics, help reduce sweat production by inhibiting the signals that stimulate sweat glands.
Glycopyrrolate: A common option for treating hyperhidrosis, particularly effective for facial and scalp sweating.
Oxybutynin: Originally used for bladder issues, has shown significant benefits in controlling excessive sweating.
Oral medications can be effective, but they may cause side effects like dry mouth or dizziness, so they’re best used under a healthcare provider's guidance.
Botox Injections
For localized sweating, such as in the armpits, hands, or feet, Botox injections offer a temporary solution by temporarily blocking the nerves that activate sweat glands, providing relief for several months. Studies have shown that Botox can reduce sweating in targeted areas by up to 87%.
Other Medical Treatments
In more severe cases, doctors may recommend treatments, such as:
Iontophoresis: A device that uses electrical currents to temporarily disable sweat glands, often used for hands and feet.
Microwave Thermolysis: A non-invasive procedure that uses thermal energy to permanently reduce sweat gland activity, particularly in the underarms.
Surgery: In rare cases, surgical interventions like sweat gland removal or sympathectomy (cutting nerves that control sweating) may be considered for extreme cases of hyperhidrosis.
When to See a Healthcare Provider
If your sweating
Soaks through clothing despite using antiperspirants,
Causes significant emotional or social discomfort, or
Is accompanied by other symptoms like weight loss or fever (which could signal an underlying medical issue),
It’s time to consult a healthcare provider. They can recommend personalized treatments that go beyond what underarm products alone can achieve.
Main Takeaways
Understanding the difference between antiperspirants and deodorants is essential for effective sweat management. Antiperspirants help manage sweat control and sweat reduction, while deodorants help neutralize odor for fresher underarms.
If over-the-counter products don’t meet your needs—particularly if you struggle with excessive sweating—consider consulting a healthcare provider about prescription-strength options.





